Fibroids are benign (non-cancerous) growths that develop in the uterus and are also referred to as fibromas, myomas or leiomyomas. Fibroids are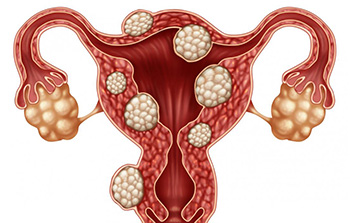 generally firm, fibrous masses, of varying size, which are made up of muscle cells within the uterus.
generally firm, fibrous masses, of varying size, which are made up of muscle cells within the uterus.
Up to 70% of women will develop fibroids by the age of 50 though many women are unaware and don’t have symptoms. Many women only become aware of the fibroids when they have a pelvic ultrasound or present to the doctor for a bleeding problem.
Types Of Fibroids
- Intramural fibroids – They develop in the muscle of the womb. If large enough, they can distort the shape of the uterus and cause heavy periods, pain and pressure.
- Subserosal fibroids – They originate in the muscle wall but protrude outside the womb into the pelvis.
- Submucosal fibroids – They grow into the inner cavity of the womb and are more likely to cause bleeding problems or difficulties when trying to conceive.
Fibroids can cause symptoms which can be classified under pressure, bleeding, or infertility. The most common symptoms include:
- Heavy or prolonged periods
- Bleeding between menstruation
- Abdominal/back/pelvic pain or discomfort
- Constipation
- Frequent urination or difficulty passing urine due to pressure on the bladder
- Abdominal distention- large fibroids might be felt by the patient
- Fertility issues
The exact cause of fibroids is unknown but they develop from rapidly multiplying uterine muscle tissue. Research has shown that these cells have more receptor for the female hormones, estrogen, and progestogen. Ultimately estrogen is responsible for the growth of fibroids and as a result fibroids tend to shrink during menopause in response to falling levels of estrogen. Fibroids are found more frequently in black women and tend to cause gynaecological problems at an earlier age in this group.
Detection & Diagnosis
Fibroids are most commonly detected during abdominal and pelvic examination but other tests are required for confirmation.
- A blood test may also be carried out to check for iron-deficiency anaemia if heavy bleeding is caused by the uterine fibroids.
- Transvaginal/ transabdominal ultrasound: The ultrasound uses sound waves to assess the size, shape and abnormalities of the uterus. It can detect uterine fibroids of all sizes, providing information on their size and location.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): This is a non-invasive procedure that creates a 2D representation of the womb. It is used to evaluate the size and location of the fibroids, in order to help determine the appropriate form of treatment.
- Computer tomography scan (CT scan): This is a non-invasive test which is more readily available than MRI and may help differentiate large fibroids from other pelvic masses, like ovarian cysts.
- Saline infusion Sonography: This test uses saline solution to distend the uterine cavity and fallopian tubes. The use of saline allows the ultrasound to detect fibroids which are either located within or indenting the uterine cavity.
- Hysteroscopy: Utilises a small telescope, inserted through the vagina and cervix, to visualise the uterine cavity. It is the gold standard for the diagnosis and treatment of submucosal fibroids.
When is treatment necessary for fibroids?
Fibroids that do not cause symptoms, are small, or occur in a woman who is nearing menopause often do not require treatment. Certain signs and symptoms may signal the need for treatment:
- Heavy or painful menstrual periods that cause anaemia or that disrupt a woman’s normal activities
- Bleeding between periods
- Uncertainty whether the growth is a fibroid or another type of tumour, such as an ovarian tumour
- Rapid increase in growth of the fibroid
- Infertility
- Pelvic pain
Can medication be used to treat fibroids?
Drug therapy is an option for some women with fibroids. Medications may reduce the heavy bleeding and painful periods that fibroids sometimes cause. They may not prevent the growth of fibroids. Surgery is often needed later. Drug treatment for fibroids includes the following options:
- Birth control pills: These drugs are often used to control heavy bleeding and painful periods.
- Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) agonists—These drugs stop the menstrual cycle and shrink the fibroids. This may allow the surgeon to remove the fibroids/uterus through a “bikini cut” rather than midline(up and down/vertical) incision. The side effect profile of GnRH agonists limits their use to 6 months and unfortunately when they are stopped, the fibroids tend to rapidly return to their original size.
- Progestin–releasing intrauterine device (IUD): This option is for women with fibroids, less the 3cm in size, that do not distort the inside of the uterus. It reduces heavy and painful bleeding but does not treat the fibroids themselves.
- Selective progesterone receptor modulators (SPRMs): This new drug rapidly reduces bleeding and permanently reduces the size of fibroids by up to 70% with repeated doses.
What types of surgery may be done to treat fibroids?
Myomectomy- the surgical removal of fibroids while leaving the uterus in place. This option preserves fertility, allowing her to still have children. Fibroids do not regrow after surgery, but new fibroids may develop, and repeat surgery may be needed later in life.
Hysterectomy- the removal of the uterus. The ovaries may or may not be removed, based on age and risk of ovarian cancer. Hysterectomy may be offered/requested when other treatments have failed, or the fibroids are very large and fertility is no longer desired.

Fibroids can reduce fertility by distorting uterine anatomy, affecting implantation and increasing miscarriages. Should the placenta implant over a fibroid, the baby may not grow as fast as it should(fetal growth restriction). Large fibroids may obstruct the passage of the baby, necessitating delivery by caesarean section or even result in heavier bleeding immediately after delivery.
