Polycystic ovary syndrome is a common condition that affects around 20% of women worldwide. The condition causes a hormonal imbalance, which affects the menstrual cycle and may make it harder for a woman to become pregnant. Due to failed ovulation, multiple small cysts build up on the ovaries and can be seen on an ultrasound scan. These cysts are just harmless follicles and aren’t a cause of cancer.
The condition usually manifests during adolescence mainly as infrequent heavy periods, as a result of a hormonal imbalance. Testosterone is produced in small amounts by the ovaries, however, women with PCOS produce higher amounts which can lead to the following problems; irregular periods, male pattern baldness, excess body hair, and infertility. In the long-term PCOS may cause diabetes and cardiac disease, this risk is reduced by maintaining a normal weight. 40% of obese patients who have PCOS have Impaired glucose tolerance and are at high risk for developing Type 2 Diabetes The exact causes of PCOS are unknown, though there may be a genetic predisposition and as such if other women related to you have PCOS then your risk of developing it is higher.
The exact causes of PCOS are unknown, though there may be a genetic predisposition and as such, if other women related to you have PCOS then your risk of developing it is higher.
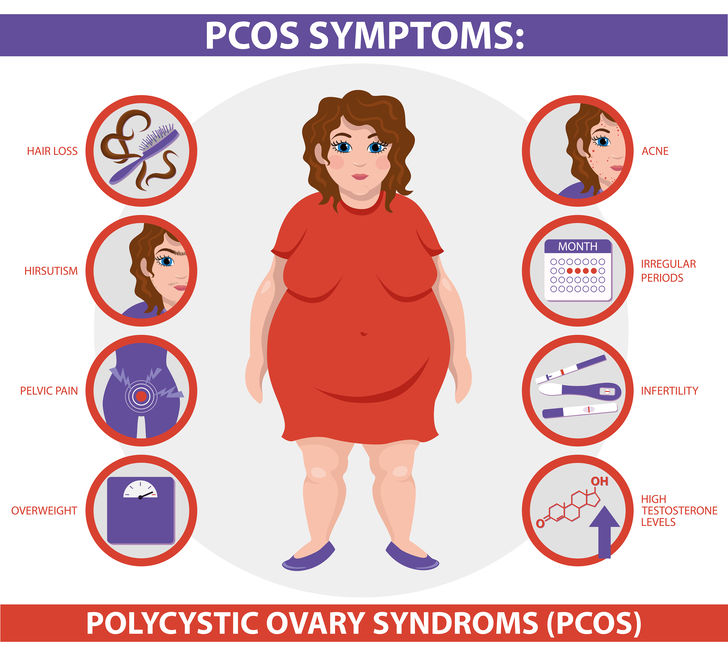
PCOS Symptoms infographic. Polycystic ovary syndrome. Detailed vector Infographic. Women Health.
Every woman is unique and women with PCOS may manifest symptoms of the disease differently. However, there are several common symptoms, including:
- Acne and oily skin
- Excessive hair growth on the face and body (hirsutism)
- Thinning hair or hair loss (alopecia)
- Weight gain and difficulty losing weight
- Irregular or no periods may be followed by significantly heavy periods
- Difficulty getting pregnant
- Depression
Having polycystic ovaries on an ultrasound scan doesn’t necessarily mean you have Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. Diagnosis requires 2 out of 3 criteria to be met :
- Irregular or no periods
- High level of testosterone on a blood test or physical signs of excessive male hormones
- Polycystic ovaries on pelvic ultrasound
- Only around 7% of women are actually diagnosed with PCOS and because it carries a risk of heart disease and type 2 diabetes, additional blood tests are required to assess lipids and diabetic status yearly
Ultimately there is no cure and treatment is tailored toward managing and reducing symptoms. The general principles are maintaining a healthy active lifestyle and normal body weight.
Weight Issues
If you are overweight losing as little as 5% of your weight through regular exercise and a balanced healthy diet, may significantly improve PCOS symptoms. Advice from a specialist dietician may be helpful in helping you reach you weight loss goals. For those who are pre-diabetic, a diet high in complex carbohydrates is advised and a dietician would be an invaluable guide.
Irregular Periods
Hormonal preparations, such as Provera or the oral contraceptive pill are usually very helpful for symptoms associated with irregular periods. Hormone containing intrauterine devices can be used instead if you want contraception. These treatment options all help in reducing the long-term risk of endometrial cancer (cancer of the lining of the womb), which is increased with less than four cycles a year.
Fertility Problems
Though many women with PCOS may become pregnant naturally, some may require medication, surgery or IVF to assist in conception. Clomiphene (Clomid), is a medication which works by encouraging the monthly release of an egg from the ovaries and is usually the first option offered to women with PCOS who are trying to conceive. If this fails, metformin may be added to increase the likelihood of success.
Surgically, laparoscopic ovarian drilling (LOD), carried out under a general anaesthetic, involves inserting a small scope through the belly button to visualise the reproductive organs. Once visualised, four needle point holes are made in the ovaries, this reduces the amount of male hormone produced and corrects the hormonal imbalance.
Excess Hair And Hair Loss
Medications, such as the birth control pill, reduce excessive hair growth by reducing the amount of male hormones circulating in your body and gradually reduces its effect on the body. This treatment usually takes 2 -3 months to take effect.
Facial hair growth can be treated with special creams or through waxing or laser treatment. Shaving may result in thicker harder facial hair. Vaniqa, Eflornithine, is a topical cream, which works by slowing down the growth of unwanted facial hair and typically a visible improvement is seen after around 6-8 weeks. (Unfortunately, not available in Trinidad at this time)
